Recently,the research article: “Designing 2D carbon dot nanoreactors for alcohol oxidation coupled with hydrogen evolution” was published in Nature Communications, and Jiangsu University is the first completed institution. Chen Qitao is the first author. Professor Mao Baodong is the first corresponding author, and Prof.Li Longhua,Yan Weicheng, Shi Weidong etc. are co- corresponding authors.
Abstract:
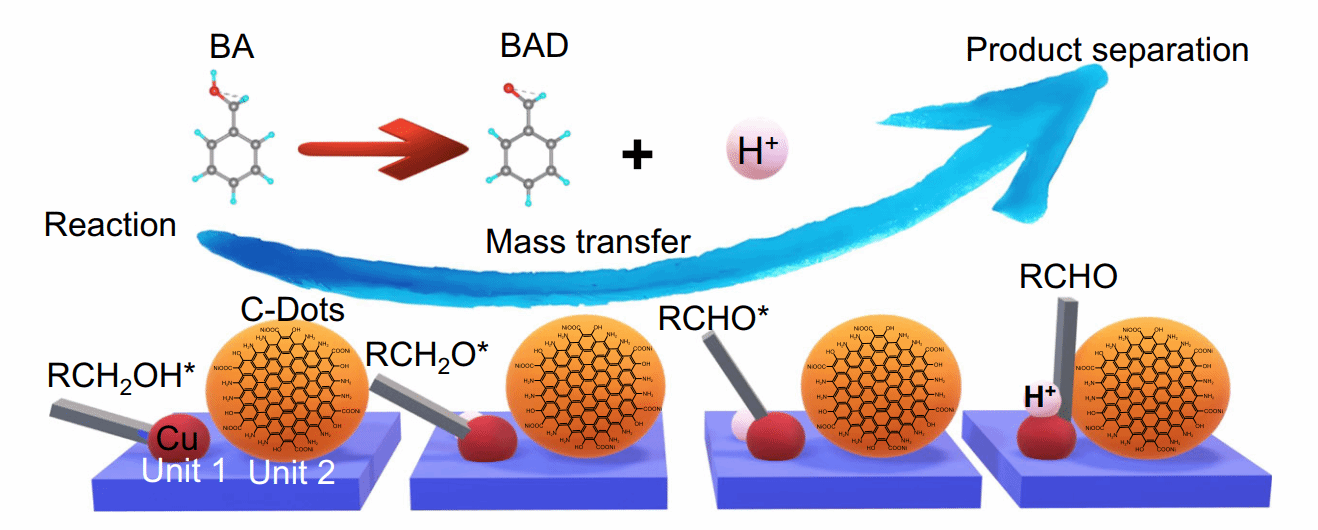
The coupled green energy and chemical production by photocatalysis represents a promising sustainable pathway, which poses great challenges for the multifunction integration of catalytic systems. Here we show a promising green photocatalyst design using Cu-ZnIn2S4 nanosheets and carbon dots as building units, which enables the integration of reaction, mass transfer, and separation functions in the nano-space, mimicking a nanoreactor. This function integration results in great activity promotion for benzyl alcohol oxidation coupled H2 production, with H2/benzaldehyde production rates of 45.95/46.47 mmol g−1 h−1, 36.87 and 36.73 times to pure ZnIn2S4, respectively, owning to the enhanced charge accumulation and mass transfer according to in-situ spectroscopies and computational simulations of the built-in electrical field. Near-unity selectivity of benzaldehyde is achieved via the effective separation enabled by the Cu(II)-mediated conformation flipping of the intermediates and subsequent π-π conjugation. This work demonstrates an inspiring proof-of-concept nanoreactor design of photocatalysts for coupled sustainable systems.
The Article Link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1038/s41467-024-52406-2